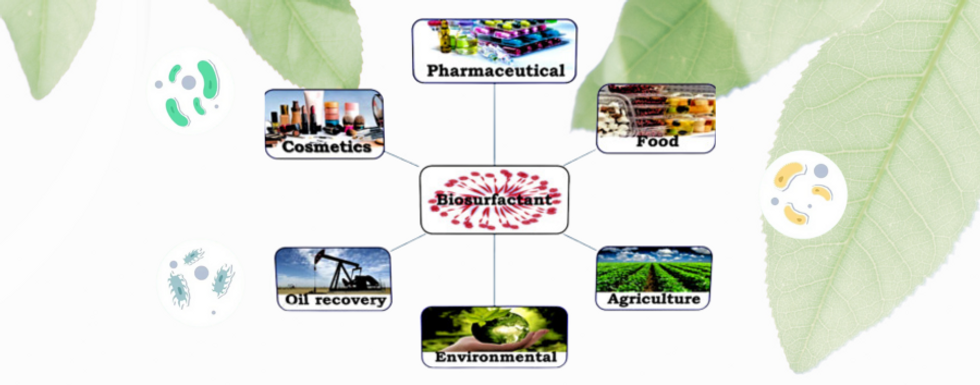
Biosurfactants
Biosurfactants are surface-active substances produced by microorganisms like bacteria, yeast, and fungi. They reduce surface and interfacial tension between individual molecules at the surface and are biodegradable, eco-friendly, and effective at extreme conditions.
Glycolipids
-
Rhamnolipids
-
Produced by: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-
Applications: Oil recovery, bioremediation, cosmetics
-
-
Sophorolipids
-
Produced by: Candida bombicola
-
Applications: Detergents, personal care products
-
-
Trehalolipids
-
Produced by: Mycobacterium spp.
-
Applications: Pharmaceutical and medical fields
-
Lipopeptides and Lipoproteins
-
Surfactin
-
Produced by: Bacillus subtilis
-
Very powerful surface tension reducer
-
Applications: Antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-tumor uses
-
-
Iturin and Fengycin
-
Produced by: Bacillus spp.
-
Applications: Agriculture, biocontrol (antifungal activity)
-




Phospholipids and Fatty Acids
-
Less efficient as surfactants
-
Found in the cell membrane
-
Applications: Used in emulsification, oil spill clean-up
Polymeric Biosurfactants
-
Emulsan (from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus)
-
Liposan (from Candida lipolytica)
-
Emulsification of hydrocarbons
-
Use in food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries








.jpg)